Chart Of Normal Blood Sugar Levels For Adults With Diabetes
Normally, your pancreas releases insulin when your blood sugar, or “ blood glucose,” gets high -after a meal, for example. that signals your body to absorb glucose until levels get back to. Normal glucose levels are important to monitor, even if you have not been diagnosed with diabetes. diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is the name of a group of diseases in which the body is unable to properly utilize blood sugar (glucose) for energy. there are three primary forms of diabetes—type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, and gestational diabetes—and, in each case, the body is.

What is a normal blood sugar level? diabetes self-management.
Diabetes mellitus is a disease that prevents your body from properly using the energy from the food you eat. diabetes occurs in one of the following situations: blood glucose levels usually return to normal after childbirth. however, women who have had gestational diabetes have an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. Normal blood sugar levels for adults with diabetes normally, your pancreas releases insulin when your blood sugar or “ blood glucose,” gets high -after a meal, for example. Chronic diabetes conditions include type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes. potentially reversible diabetes conditions include prediabetes and gestational diabetes. prediabetes diabetes normal occurs when your blood sugar levels are higher than normal, but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. A normal a1c level is below 5. 7%, a level of 5. 7% to 6. 4% indicates prediabetes, and a level of 6. 5% or more indicates diabetes. within the 5. 7% to 6. 4% prediabetes range, the higher your a1c, the greater your risk is for developing type 2 diabetes.
Diabetes Wikipedia
Diabetes mellitus (dm), commonly known as diabetes, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level over a prolonged period of diabetes normal time. symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst, and increased appetite. if left untreated, diabetes can cause many complications. acute complications can include diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, or. Anyone older than age 45 is advised to receive an initial blood sugar screening, and then, if the results are normal, to be screened every three years thereafter. women who have had gestational diabetes are advised to be screened for diabetes every three years. anyone who has been diagnosed with prediabetes is advised to be tested every year. Normal less than 140 mg/dl: prediabetes 140 mg/dl to 199 mg/dl: diabetes 200 mg/dl or higher: random (also called casual) plasma glucose test. this test is a blood check at any time of the day when you have severe diabetes symptoms. diabetes is diagnosed at blood sugar of greater than or equal to 200 mg/dl;. help sick kids 21 september 2015 living a normal life diabetes monitoring 21 september 2015 nmmc promotes healthy workforce
Mar 27, 2018 · the answer to the question what is a normal blood sugar level is as follows: fasting normal blood sugar normal for person without diabetes: 70–99 mg/dl (3. 9–5. 5 mmol/l) official ada recommendation for someone with diabetes: 80–130 mg/dl (4. 4–7. 2 mmol/l) normal blood sugar 2 hours after meals. Normalblood sugar levels for adults with diabetes diabetes normal normally, your pancreas releases insulin when your blood sugar or “ blood glucose,” gets high -after a meal, for example.
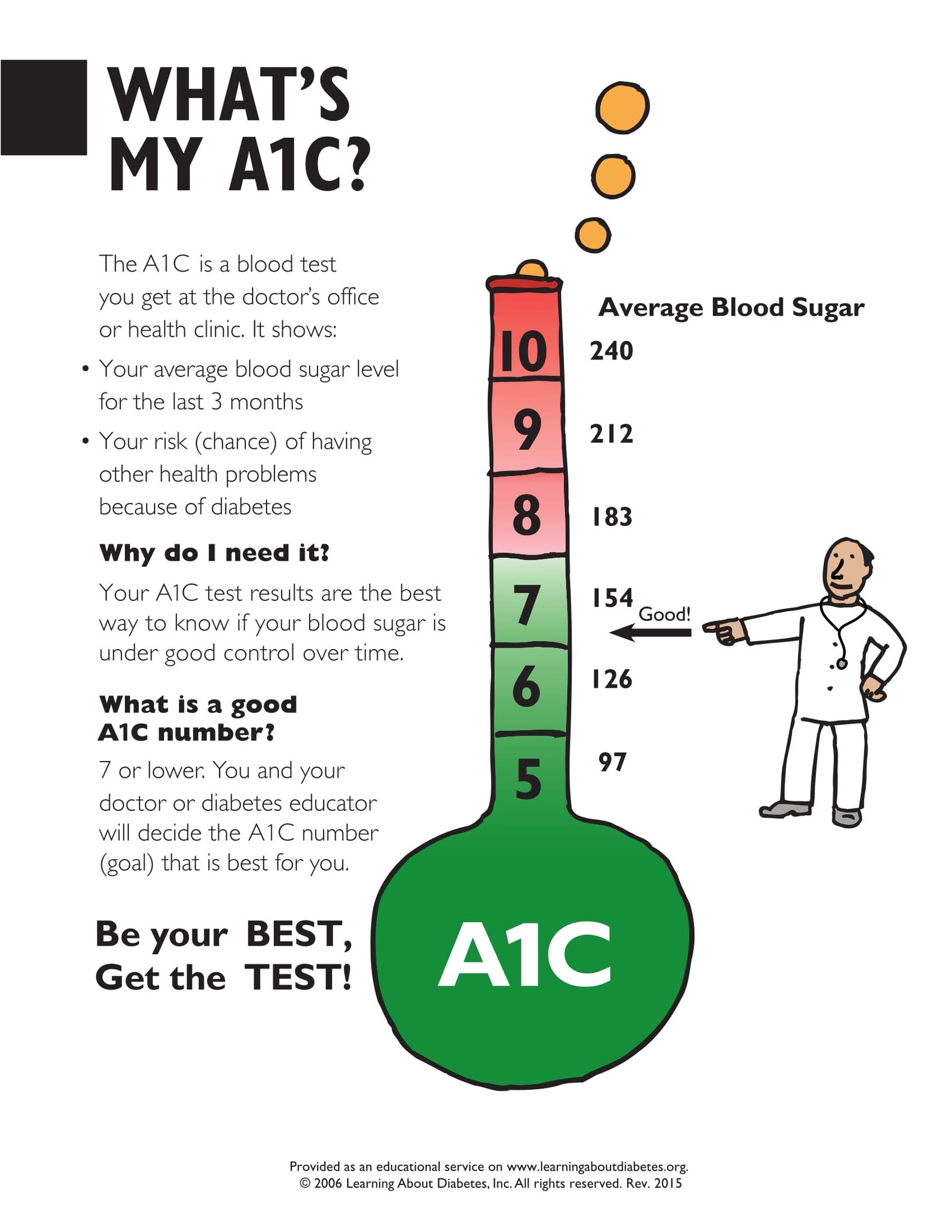
Understanding blood glucose level ranges can be a key part of diabetes self-management. this page states ‘normal’ blood sugar ranges and blood sugar ranges for adults and children with type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes and blood sugar ranges to determine people with diabetes.. if a person with diabetes has a meter, test strips and is testing, it’s important to know what the blood glucose. normal) guinea pig(normal) hamster(normal) human(adult normal) human(diabetes) human(heart diseases) human(liver cirrhosis) human(lung tumor) guinea pig(normal) hamster(normal) human(adult normal) human(diabetes) human(heart diseases) human(liver cirrhosis) human(lung See full list on mayoclinic. org. Long-term complications of diabetes develop gradually. the longer you have diabetes — and the less controlled your blood sugar — the higher the risk of complications. eventually, diabetes complications may be disabling or even life-threatening. possible complications include: 1. cardiovascular disease. diabetes dramatically increases the risk of various cardiovascular problems, including coronary artery disease with chest pain (angina), heart attack, stroke and narrowing of arteries (atherosc
Before people develop type 2 diabetes, they almost always have "prediabetes"—blood sugar levels that are higher than normal but not yet high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes. doctors sometimes refer to prediabetes as impaired glucose tolerance (igt) or impaired fasting glucose (ifg), depending on what test was used when it was detected. Jun 11, 2019 · a normal fasting blood glucose for someone who does not have diabetes ranges from 70 to 99 mg/dl. the american diabetes association recommends a routine screening for type 2 diabetes starting at age 45. if the results are normal, the screening should be repeated every 3 years.
The answer to the question what is a normal blood sugar level is as follows: fasting normal blood sugar normal for person without diabetes: 70–99 mg/dl (3. 9–5. 5 mmol/l) official ada recommendation for someone with diabetes: 80–130 mg/dl (4. 4–7. 2 mmol/l) normal blood sugar 2 hours after meals. Diabetic patients have a higher prevalence of thyroid disorders compared with the normal population. Diagnosing diabetes how is diabetes diagnosed? diabetes is diagnosed with fasting sugar blood tests or with a1c blood tests, also known as glycated hemoglobin tests. a fasting blood sugar test is performed after you have had nothing to eat or drink for at least eight hours. normal fasting blood sugar is less than 100 mg/dl (5. 6 mmol/l).
Normal fasting blood sugar for person without diabetes. a normal fasting blood glucose for someone who does not have diabetes ranges from 70 to 99 mg/dl. the american diabetes association recommends a routine screening for type 2 diabetes starting at age 45. if the results are normal, the screening should be repeated every 3 years. With type 2 diabetes, your body doesn’t use insulin well and can’t keep blood sugar at normal levels. about 90-95% of people with diabetes have type 2. it develops over many years and is usually diagnosed in adults (but more and more in children, teens, and young adults). Mother of a diabetic child provides detail on juvenile diabetes and normal blood sugar levels. includes the family''s journey, support system, and recipes. Type 1 diabetes can't be prevented. however, the same healthy lifestyle choices that help treat prediabetes, type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes can also help prevent them: 1. eat healthy foods. choose foods lower in fat and calories and higher in fiber. focus on fruits, vegetables and whole grains. strive diabetes normal for variety to prevent boredom. 2. get more physical activity. aim for 30 minutes of moderate physical activity a day. take a brisk daily walk. ride your bike. swim laps. if you can't
Subscribe by Email
Follow Updates Articles from This Blog via Email


No Comments